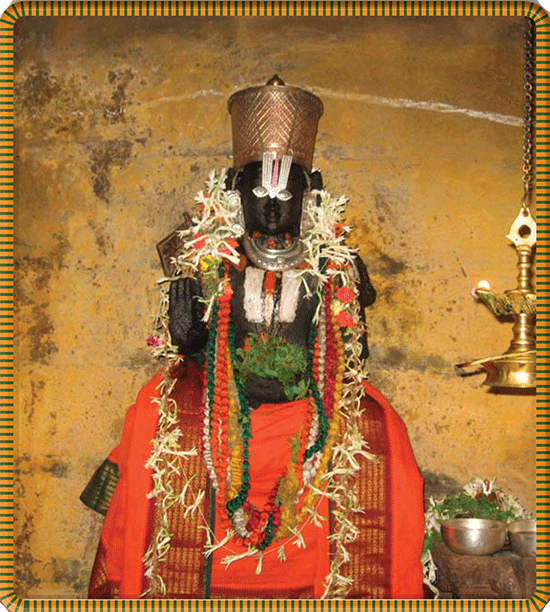
SURI KESHAVA SOMAYAJULU AND HIS WIFE KANTHIMATHI , a young orthodox Vaishnavite couple living in Sriperumbudur (30 miles southwest of modern-day Chennai), yearned for a child. As so many young Hindu couples before them, the two regarded birth as a blessing held in the hands of God. Together they prayed ardently to the Varadaraja Perumal Deity in nearby Kanchipuram. Their heartfelt prayers were answered by the birth of a healthy, divine child—a son who, according to legend, was an incarnation of the serpent Adishesha (who had long ago incarnated as Rama’s younger brother, Lakshmana). §
SURI KESHAVA SOMAYAJULU AND HIS WIFE KANTHIMATHI , a young orthodox Vaishnavite couple living in Sriperumbudur (30 miles southwest of modern-day Chennai), yearned for a child. As so many young Hindu couples before them, the two regarded birth as a blessing held in the hands of God. Together they prayed ardently to the Varadaraja Perumal Deity in nearby Kanchipuram. Their heartfelt prayers were answered by the birth of a healthy, divine child—a son who, according to legend, was an incarnation of the serpent Adishesha (who had long ago incarnated as Rama’s younger brother, Lakshmana). §
Kanthimathi’s brother, Thirumalai Nambi, struck by his nephew’s noble appearance and brilliant aura, named him Ramanujan (brother of Rama). Also named as Ilaya Perumal (“younger God”) by Nambi, Ramanuja would grow up to became a great scholar, teacher, theologian, philosopher and social reformer. Born ten centuries before Mahatma Gandhi, he foreshadowed Gandhi’s vision and ideals. He believed that the holy scriptures and Lord Narayana, God, are not the sole property of the brahmin community. Rather, everyone, irrespective of social status, has the right to learn the scriptures and worship Narayana. He believed that service to humanity is service to God. §
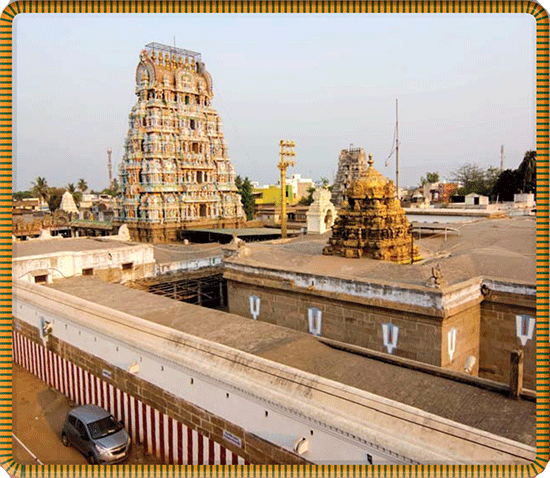
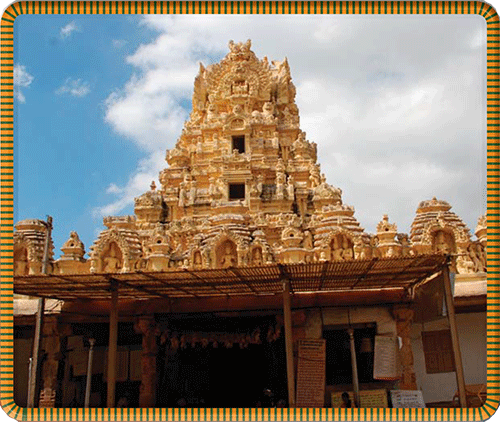
A view of the temples in Sriperumbudur. The largest tower is one of the gopurams of the Adhikesava Perumal temple.§
Ramanuja and His First Teacher, Yadavaprakasha §
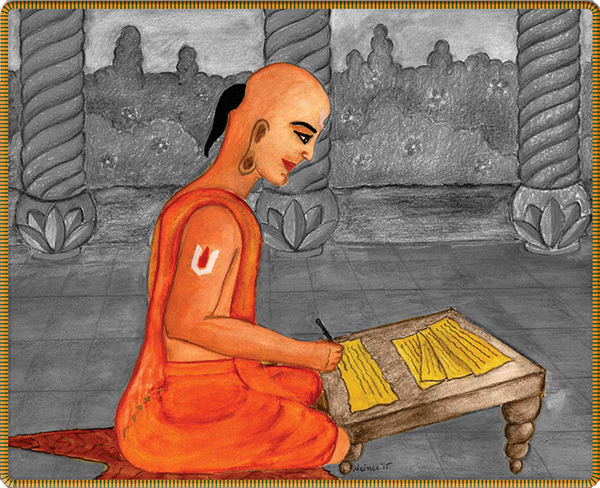
Young Ramanuja had an extraordinary and precocious gift for grasping the meaning of the most difficult Sanskrit texts. He sought out the company of wise men, scholars and devotees. Ramanuja’s family arranged his marriage at age 16 to a beautiful girl named Rakshambal, culminating in a week-long ceremony at which the whole town rejoiced. But the joy did not last long, as Ramanuja’s father, Keshava, fell severely ill and died shortly after. §
Following the traumatic demise of his father, the young groom left Sriperumbudur with his wife and mother and moved to the neighboring town of Thiruputkuzhi, near Kanchipuram, a well-known center of learning. Having studied Sanskrit and the Vedas under his father, he would now study advanced Vedanta. There, Yadavaprakasha, a renowned advaitic acharya, accepted Ramanuja and his cousin Govinda as his disciples. §
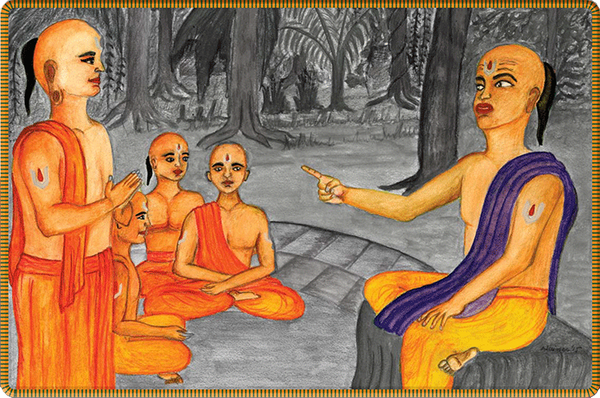
There is a saying in Tamil, “Guruvukku minjina sishyan,” praising the exceptional student who in some way surpasses his guru. Ramanuja was one such student. Yadava was strict in his beliefs, demeanor and expectations, demanding complete, unquestioning devotion from his disciples. Though faced with an intimidating teacher’s unbending ways, Ramanuja could not suppress his profound disagreement with Yadava’s views. §
For instance, he openly challenged the teacher on the meaning of “Satyam, Jnanam, Anantam Brahma” (Taittiriya Upanishad 2.1.1). Yadava’s interpretation was, “Brahman is the whole form of truth, wisdom and infinitude.” Ramanuja’s gleaning was much fuller: “Lord has qualities such as truth and knowledge and has no beginning or end. God is eternal. However, those qualities alone are not Brahman.” §
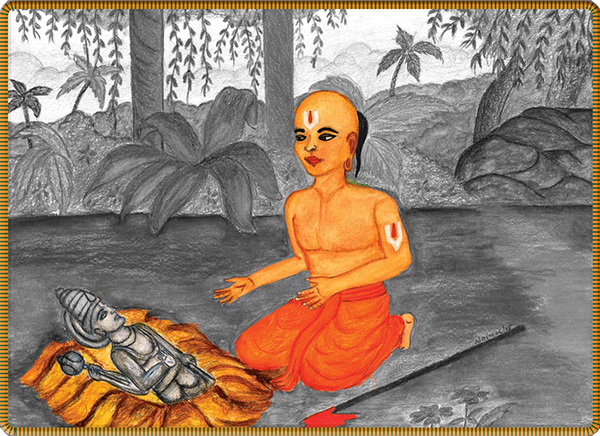
Yadavaprakasha was not impressed with his disciple’s extension or interpretation of the text, but rather annoyed. He was afraid that his brilliant student was a real threat not only to his status as guru but also to his advaita philosophy. Concerned that, if allowed to thrive, the youth might found a rival school, the guru hatched a plot to kill Ramanuja during a pilgrimage to Varanasi that he would make with all his disciples. The plan was to drown Ramanuja near Manikarnika Ghat. According to Life of Ramanujan, Yadav rationalized this as a “death which, taking place in the Holy Ganga, would be counted as an affair of merit, which they thought would not involve the actors in sin! What travesty of spiritual ethics by Yadava!”§
Ramanuja has a heated philosophical debate with his first teacher, Yadavaprakasha (seated on bench), who scolds the impertinent student.§
Along the way, Ramanuja’s cousin Govinda learned of the murderous plot and informed Ramanuja. Shocked and fearful of his teacher’s intent, Ramanuja fled the party, hiking off into the Vindhya hills. Traveling through the forest, he met and was befriended by a hunter couple who said they were on pilgrimage south to Kanchipuram. He shared that he wanted to go to Kanchi as well, and they offered to take him there. They suggested a well they knew of where they could gather water and bathe. They camped for the night and the next morning hiked to the well. Ramanuja went down a hill to the well and drank of the cool water. When he returned with water for the hunter couple, he could not find them. The couple had disappeared. Weary and confused, he continued his journey. Approaching a town and seeing its temple towers, he recognized it as his beloved Kanchipuram. Suddenly it dawned on him that the hunter couple were not human but divine beings. The Deity Varadaraja Perumal of the Kanchi Temple and His consort Perundevi had become his guides in the Vindhyan wilds and that night while he slept had miraculously transported him 1,000 miles to his destination. §
South India’s Four Renowned Philosopher Saints
 indu faith, religion, ethics, culture and traditions are strongly rooted in the vast body of ancient scriptures called the Vedas. Hindus revere these scriptures, compiled thousands of years ago, as revealed truth, or shruti (“that which is heard”). The first sections of the Vedas represent the karma kanda, emphasizing human life and worship of the Divine. The final portion of the Vedas, the Upanishads, being philosophical by nature, represent the jnana kanda (wisdom), emphasizing philosophy. They are also considered the ultimate end of the Vedas; hence the term Vedanta (Veda + anta, meaning “end”). The Upanishads speak of the nature of reality, the world and the soul’s path to liberation from rebirth.§
indu faith, religion, ethics, culture and traditions are strongly rooted in the vast body of ancient scriptures called the Vedas. Hindus revere these scriptures, compiled thousands of years ago, as revealed truth, or shruti (“that which is heard”). The first sections of the Vedas represent the karma kanda, emphasizing human life and worship of the Divine. The final portion of the Vedas, the Upanishads, being philosophical by nature, represent the jnana kanda (wisdom), emphasizing philosophy. They are also considered the ultimate end of the Vedas; hence the term Vedanta (Veda + anta, meaning “end”). The Upanishads speak of the nature of reality, the world and the soul’s path to liberation from rebirth.§
In scripture it is proclaimed, “Acharya devo bavah:” “Acharya (guru) is God,” implying that only with the guidance of an acharya can one comprehend and interpret the holy scriptures, lead a righteous life and use jnana, or knowledge, as a vehicle to attain moksha. The four great acharyas of South India, who lived many centuries ago, are Shankara, Ramanuja, Nimbarka and Madhva. Each formulated his own interpretation of the relationship between the infinite God (Paramatman, Parabrahman, Purushothaman, etc.) and the finite atman (individual self), as revealed in the Upanishads and other texts. The three basic concepts in their philosophies are God, soul and world—the fundamental triad of existence.§
These four acharyas were not contemporaries: Ramanuja (1017–1137 ce) could question the interpretation of Shankara (780–812) but not of Madhva (1238–1317) or Nimbarka (13th century). Nor were they of the same faith: Ramanuja, Madhva and Nimbarka were staunch Vaishnavites, while Shankara was of the Smarta tradition. §
Shankara promulgated pure Advaita, a non-dualistic or monistic philosophy teaching the oneness of the soul, atman, with Paramatman, the Supreme Soul, or God, and focusing on Reality as transcendent. Madhva, at the other extreme, taught Dvaita, a dualistic and theistic philosophy, postulating an eternal distinction between atman and Paramatman. He regarded the Supreme Person as a great Being, a Personal Lord. Nimbarka taught Dvaita-Advaita, positing three equally real and co-eternal realities—Brahman, the souls (chit), and the world (achit). Brahman is the Controller (niyantri), chit is the enjoyer (bhoktri) and the achit is the object enjoyed (bhogya). Ramanuja’s philosophy, known as Vishishtadvaita, or “monism of the qualified,” finds a middle ground, leaning towards monism yet disagreeing with Shankara’s understanding on several points: the relationship between atman and Paramatman; the definition of Parabrahman as nirguna (without guna, qualities) and the concept of maya, which Shankara defined as illusion. Ramanuja’s Vishishtadvaita synthesizes the Advaita philosophy with the devotional practices of dualists and the alvar saints’ path of surrender, saranagati.§
When Yadavaprakasa arrived at Kanchi, to his astonishment and dismay he found Ramanuja there ahead of him. Feigning joy, he said, “Our grief at your loss in the wilds was great; but seeing you now, it has given way to boundless joy.” Ramanuja reported to his would-be assassin that he had lost his way and gotten separated from the group, but was aided by a hunter couple who had magically transported him to Kanchipuram while he slept under a tree. Hearing this account, Yadava stared at Ramanuja in fear and wonder, at that moment realizing that Ramanuja was not an ordinary man but a great soul to be looked upon with utmost regard. Ashamed of his evil intentions, Yadava invited Ramanuja to again grace his school with his presence.§
Ramanuja resumed his studies with Yadava, but their relationship once again became bitter as philosophical differences kept them at odds. When Ramanuja could no longer endure his guru’s intellectual tyranny, he left him. The following incident, narrated by Swami Tapasyananda in his book Sri Ramanuja, illustrates their divergent perspectives: §
Ramanuja kneels beside Yamunacharya, who has just left his body. The thumb and two fingers on the right hand are clenched, which Ramanuja interprets as three wishes he must fulfill.§
“One day Yadavaprakasha was interpreting the Upanishadic passage, Sarvam khalvidam brahma, ne’ha nanasti kinchana, ‘All this is Brahman; there is no diversity here whatever.’ He was interpreting it, justifying the doctrine of the oneness of the Atman and Brahman. Ramanuja differed from him and said the passage would have meant the oneness of all with Brahman if it were not followed by, Tajjalan iti shanta upasita, ‘This universe is born in, sustained by and dissolves in Brahman; meditate thus on Him.’ This qualification makes the earlier part mean: ‘The things in this samsara are not existing severally, but as pearls strung on a thread; they are interpenetrated by Brahman and held as a unity without impairing their manifoldness.’ This interpretation of Ramanuja generated a violent fit of annoyance in Yadavaprakasha. He asked Ramanuja to get away from his school. In obedience to the teacher, he took leave of him after worshiping his feet in all reverence.”§
This was a turning point in the young philosopher’s life. Years later, Ramanuja defeated this former master in a debate. So potent was the victory that the once arrogant advaitin became a staunch Vaishnavite and a devotee of Ramanuja.§
“Ramanuja was glad to leave this teacher of an impossible and absurd philosophy. Straight home he went, and informed his mother Sri-Devi of all that happened. ‘Enough of thy studies, son!’ said she; ‘there is Tirukkacchi Nambi who is in great favor with Lord Varadaraja. Seek his advice and service, and abide by his will. That will do thee all the good.’ Ramanuja at once sought Nambi and besought him to employ him in divine services in the temple” (as recounted in Govindacharya’s The Life of Ramanujacharya).§
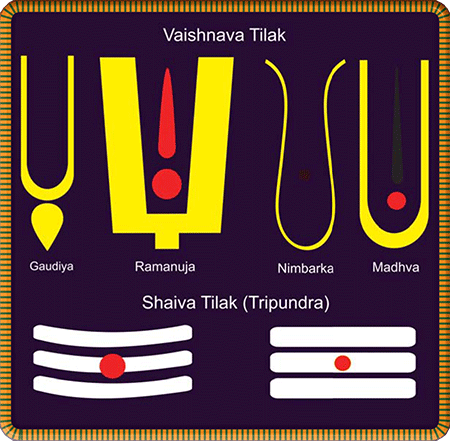
The distinctive sectarian forehead ¨ body insignia of four Vaishnava denominations along with the tripundra tilak worn by Saivites.§
Ramanuja and the Great Yamunacharya§
After leaving Yadavaprakasha, Ramanuja searched for a spiritual master. Meanwhile, the renowned Yamunacharya (917-1042) of Srirangam, now ailing, had been looking for an ideal student to become his successor. Yamunacharya was a scholar, a spiritual master and a powerful debater. As a mere child of twelve, he had defeated the most formidable scholar at the king’s court, winning half the kingdom and receiving the title Alavandar (“ruler,” “savior”) from the queen. Yamuna later renounced the kingdom to become a sannyasin and acharya, fulfilling the wishes of his grandfather, the great Nathamuni. It should be mentioned that the Vishishtadvaita philosophy and the creed of Shri Vaishnavism were already well established in South India at this time, firmly embodied in important temples at Kanchipuram, Tirupati and other major towns. The prefix Shri refers to the Goddess Lakshmi, consort of Vishnu. Yamuna was in charge of the Ranganatha Temple and Vishishtadvaita Math at Srirangam, the main center of the Shri Vaishnavas.§
It is believed that Ramanuja’s break with Yadavaprakasha was due to the prayers of Yamunacharya. Having had heard of his saintly prowess, Yamunacharya foresaw him as his successor. Author Govindacharya narrates this prayer: “Yamunacharya now mounted up to the central shrine of Lord Varada (called Hastigiri). Standing before the Deity he prayed, ‘Great Lord! grant me a boon. Thou art Vara-da (Boon-Granter). By thy favor, the deaf hears, the lame runs, the dumb speaks, the blind sees and the barren bears. I have sought Thee. Grant me that Ramanuja shall become the bearer of the torch of our faith.’”§
Ramanuja’s Philosophy & Theology
 amanuja, in contrast with Shankara, asserts that the Upanishadic absolute Brahman is not a bare identity or a non-entity but rather a determinate whole, maintaining an identity in and through the differences—that the absolute, infinite Brahman manifests in every finite reality. He echoes the words of Prahlad, who defied his atheist father by saying God is in this pillar and even in the smallest of all things (“Thoonilum ullan, thurumbilan ullan”). Life is real, matter is real, and universe is real; these are not figments of imagination, not illusory objects, however transient they may be. Ramanuja’s personal Deity is a composite of the divine characteristics described in the holy Sanskrit scriptures and the Tamil Divya Prabandham. The Supreme has “a divine form peculiar to itself, not of the primal substance or matter (prakriti) and not due to karma.” §
amanuja, in contrast with Shankara, asserts that the Upanishadic absolute Brahman is not a bare identity or a non-entity but rather a determinate whole, maintaining an identity in and through the differences—that the absolute, infinite Brahman manifests in every finite reality. He echoes the words of Prahlad, who defied his atheist father by saying God is in this pillar and even in the smallest of all things (“Thoonilum ullan, thurumbilan ullan”). Life is real, matter is real, and universe is real; these are not figments of imagination, not illusory objects, however transient they may be. Ramanuja’s personal Deity is a composite of the divine characteristics described in the holy Sanskrit scriptures and the Tamil Divya Prabandham. The Supreme has “a divine form peculiar to itself, not of the primal substance or matter (prakriti) and not due to karma.” §
To illuminate the acharya’s brilliant outlook, we gratefully offer the following long excerpt from the book Sri Ramanuja, by Swami Tapasyananda of the Ramakrishna Mission.§
.....................§
The philosophy of Sri Ramanuja is the most pre-eminent among the Bhakti Schools of Vedanta, both because of the profundity of the doctrines it expounds and the balanced devotionalism it teaches. Barring Bhaskara’s Bhedabheda (identity-in-difference) interpretation of Vedanta Sutras, Ramanuja’s was the first comprehensive criticism of the Vedanta as expounded by Shankara some three centuries before him. The other schools of Bhakti Vedanta that came after him have only taken up his criticisms and teachings with minor re-statements to suit their theological leanings. The common object of all these systems may be stated thus: They seek to establish the supremacy of the Divine Personality, known under the different sacred names of Purushottama, Narayana, Vasudeva, Krishna, etc., and equate Him with Brahman, the Absolute of the Upanishads. For them, the Supreme Being is a Person with attributes, and there is no Absolute beyond Him. They also lay stress on the exclusive position of devotion and Divine grace as the only means to overcome the hold of karma on the jiva and enable him to attain salvation. Salvation or release from the hold of karma does not mean for them the mergence of the jiva in Brahman, but attaining to the status of an eternal servant of His, which alone can give unalloyed bliss to the jiva. Most of these teachings are mainly theological, but they require the backing of a consistent metaphysics to establish their credibility.§
Among all the teachers of this devotional brand of Vedanta, Ramanuja is the one whose metaphysical genius rivals that of Shankara himself. He was a master of Vedic lore and methodology of arguments and exposition. While in his subsidiary works he leans very much on the devotional writings of his school of Vaishnavism, in his main work, the Shri Bhashya or the commentary on the Vedanta Sutras of Badarayana, he exhibits himself to be a pure Vedantin, that is, the follower of the Upanishadic doctrine of Brahman, which of course is for him identical with Narayana, the Divine Person.§
The Upanishadic Brahman is the unity which comprehends in Himself all the diversities of common experience and yet remains unaffected and unlimited by them. Shankara establishes that unity by reducing all diversity into a mere appearance like a snake superimposed on a rope in semi-darkness. According to him, the darkness of ignorance is the cause of illusory presentation of multiplicity. All the time the multiplicity is perceived, it is not actually there, and the unitary Consciousness had remained unchanged. On the light of knowledge arising, the illusory presentation disappears without leaving any residue beyond the Non-dual One, which was always there unchanged as the substratum. He thus achieves the unity of all existence and the unchangeableness and unaffectedness of Brahman. This achievement leaves many problems unsolved and creates many others to be solved. He however gives a prima facie reality to the world of diversity from the practical point of view (vyavaharika satta), only to deny it absolutely in the end. An unmodified and attributeless Consciousness alone is the Ultimate Reality. Reality has thus for him two tiers—the apparently real and the truly real.§
Ramanuja is totally hostile to this Advaitic interpretation of the unity proclaimed by this brand of Vedanta. Unity is not the sublation of all diversity but the subordination of diversity to unity. His system is called Vishishtadvaita, a term which, according to competent authorities, is not used by him anywhere in his writings, but came to be used later to differentiate it from the other systems of Advaita, just as Shankara’s doctrine came to be called in later times Kevaladvaita. Both Shankara and Ramanuja considered themselves only as Vedantins, and for both of them their system is the Vedanta. §
The term Vishishtadvaita is often translated as “qualified non-dualism.” Scholars disagree with this translation. The compound (sandhi) is not karmadharayan but bahuvrahi, and its English translation will be the “non-duality of the qualified whole.” Von Buitenin has elaborated it as “unity of the universe’s spiritual and non-spiritual substances with, and in, a God whom they modify as His body.” A more compact translation is “pan-organistic non-dualism.” In this system, the world is ultimately true, the jiva is ultimately true, God is ultimately true, and liberation from bondage is also factually true. Thus, in effect, it is a totally realistic theism in which God and the Absolute are one and the same. The non-dual, all-inclusive qualified Whole is the Brahman of the Vedanta, according to Ramanuja.§
While this metaphysical framework is established and argued with relentless logic and philosophical methodology of Vedantic tradition, Ramanuja’s system gets flesh and blood by his devotional ideologies of the passionate devotees of the Lord Vishnu (the alvars) that the Tamil land produced from the second to the eighth century. Thus Ramanuja’s Vedanta becomes philosophical Vaishnavism. While he is a strict Vedantin in his methodology and way of scriptural exegesis, he identified the Upanishadic Brahman with Vishu-Narayana; and this is his turning point from philosophy to religion. His Vaishnavism is indicated in his early major writing the Shri Bhashya, but becomes pronounced in his later writings. The account of Ramanuja’s life given earlier makes clear how these two streams of thought, the Vedic and the Vaishnava, came to mingle in him.§
Theology§
In fact, Ramanuja’s mission in life was this—to effect a rational and natural mingling of the rapturous devotion of the alvars with the Upanishadic quest of the ontological and unifying ground of the changing world of the many. Bhakti, or devotion, requires two—the adorable and lovable God who is a Person as also the Supreme Being on the one hand, and the devotee who finds his fulfilment in service of Him, on the other. The Vedanta of the Upanishads mainly preaches the doctrine of the Absolute Being, who is the non-dual source, substratum and dissolving ground of the many that constitute the world of our experience. “That out of which all beings come, in which they all subsist, and into which they are withdrawn is Brahman”—this is the watchword of the Upanishads. Brahman is all-inclusive and all-absorbing, and is described by such epithets as Sat-chid-ananda (Existence-knowledge-bliss) and Satyam, Jnanam, Anantam Brahma (Brahman is Truth, Consciousness and Infinite). §
Shankaracharya interprets this Upanishadic doctrine of the Absolute as the Non-dual Being in whom the world of the many is a mere appearance ascribed by Ignorance and not actually existing. For practical purposes, he gives a prima facie reality (Vyavaharika Satta) to the world of the many and to God, who is its cause. But this God (Saguna-Brahman) is distinguished from the Absolute, and His reality belongs to the same order as that of the world of the many that are said to be His creation. When Ignorance is overcome by proper metaphysical insight, the aspirant realizes that what he considered as his “I” is really the Absolute Brahman into whom the apparent world and its God too resolve. It is comparable to the appearance of a snake in semi-darkness, and its disappearance in its substratum, the rope, on the removal of darkness. Both the world and God conceived as its cause are sublated and are realized as having had no real existence.§
Ramanuja totally differs from such interpretation of the Upanishadic doctrine which militates against the ultimacy of God and the supremacy of devotion. He criticises severely the theory of Ignorance and the compartmentalisation of Reality into Paramartha (ultimate) and Vyavaharika (relative or practical). To the question, what is the locus of Ignorance, there is no credible answer from the Advaitin. If it is Brahman, Brahman becomes loaded with evil and becomes unworthy as a spiritual goal. If it is the jiva (individual spirit), the same defect persists, as the jiva in its real nature is one with Brahman according to advaita. If it is an entirely different category, dualism is the result. Besides, the jiva is caused by the upadhis (adjuncts) superimposed on Brahman, and these upadhis are the products of Ignorance. Thus Ignorance must precede the jiva and cannot therefore be conceived as located in it. To describe Ignorance as a category that is neither existent nor non-existent nor a combination of both is to speak a language unknown to logical thinking.§
Ramanuja directs a devastating attack against the doctrine of a sublatable God who is less than the Absolute or the Supreme Being, against the theory of Ignorance which is without a definite locus and which cannot be described as existent or non-existent or a combination of both, and against the compartmentalization of Reality into Paramartha (the ultimately real) and Vyavaharika (the relatively real), which means only that the latter is illusory.§
Ramanuja’s greatness consists in bringing to bear his Sanskritic and Veda-oriented ideology and methodology on the purely devotional heritage of the alvars, and thus creating what is called Ubhaya-Vedanta [meaning two-fold Vedanta], which is significant in the whole world of philosophy, as also in the limited sphere of the Tamil land.§
As explained by Swami Tapasyananda, “It was his great ambition to bring about a union between the emotional religion of the alvars and the Vedantic methodology of philosophic exposition which had become current in the scholarly world after the advent of Shankaracharya and his commentaries on Vedantic texts. He could not himself fulfill this work in his life, but towards the end of his life he came across Ramanuja and recognized in him the competent Vedic scholar who could do it.” Overjoyed upon hearing of Ramanuja’s separation from his former guru, Yamuna sent Mahapurna, one of his closest disciples, to go and bring the brilliant student to him from Kanchipuram. §
Reaching Srirangam after four days of travel, Ramanuja and Mahapurna encountered a long funeral procession which they learned was carrying the body of Yamuna to the cremation grounds. Despite his will to live until Ramanuja’s arrival, the great Vaishnava saint had passed away. §
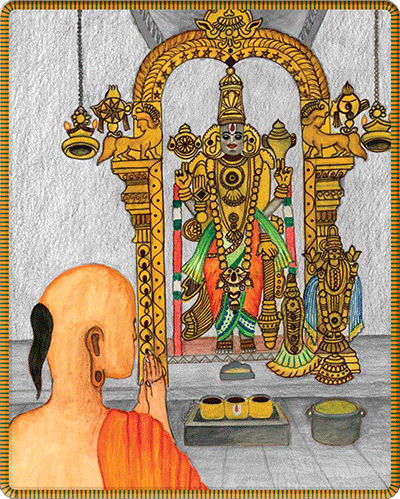
The murti of Sri Ramanuja inside the Adikesava Perumal Temple at his birthplace, Sripurembudur.§
Hearing this tragic news, Mahapurna and Ramanuja fell to the ground and wept. After a few moments, forgetting his own grief, Mahapurna led Ramanuja by the hand to Yamuna’s side. “I have at least been able to see Yamunacharya,” Ramanuja uttered. Falling silent, he scanned the body and discovered that the thumb and two fingers of the right hand were curled. Intrigued by the strange sight, Ramanuja wondered if the sage had some special message to express, and asked aloud to the gathering if the guru had told them of some important wishes that had been unsatisfied in his life. Mahapurna then explained to Ramanuja that, yes, indeed, his Acharya had many times expressed three aspirations: §
1) To perpetuate the doctrine of saranagati, complete surrender to the personal Deity; 2) To write a commentary on the Brahma Sutras of Sage Vyasa to bring out the real Vishishtadvaita meaning within them; 3) To perpetuate the names of Parashara (author of Vishnu Purana) and saint Shadakopa (a poet-saint also known as Nammalvar). §
Without hesitation, Ramanuja promised boldly that he would fulfill these ambitious goals. “‘Holy sage,’ addressing his figure, ‘if this is thy mind, I promise I shall carry it out, provided I have the health, provided thy grace is on me, and provided God grants my prayers.’” (Govindacharya).§
And as he did so, the saint’s curled fingers straightened one by one. At that moment, Ramanuja accepted Yamunacharya as his manasika acharya, “silent teacher.” Witnessing these vows and the miraculous uncurling of Yamunacharya’s fingers, the whole assembly in one voice declared, “Sire, doubt not that the sage’s grace is fully upon you; the very power and glory of his spirit will enter into you; you are the fit successor to him for furtherance of our faith. We all anoint you for the task.” Once the funeral rites were performed, Ramanuja took leave of Mahapurna. §
Yamunacharya’s death was a severe blow to Ramanuja; he left for Kanchi without even seeing Lord Ranganatha. It is chronicled of Ramanuja that he often used to express to his holy assembly that “If I had been permitted for one single day to be in the living company of Sri Yamuna, I would have constructed a staircase to Heaven and procured free admission to all thereto” (Govindacharya).§
Transcending Social Barriers§
Social structure in eleventh-century India was quite different from what it is now. Only members of the brahmin caste were allowed to perform puja in Hindu temples. And the lowest members of the social hierarchy, the untouchables, were not allowed to enter temple premises at all. Brahmins did not entertain non-brahmins in their homes. Ramanuja had no regard for the caste system, and he never ceased seeking instruction from those who were qualified to give it, regardless of caste. §
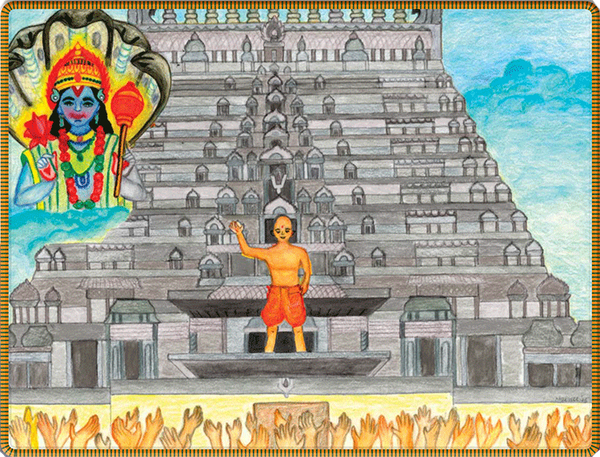
Standing at the base of a temple gopuram just moments after his japa initiation, Ramanuja shouts out to the masses the sacred and secret mantra Om Namo Narayana.§
After the cremation of Yamuna, Ramanuja returned to Kanchi where he devoted his time to serving Lord Varadaraja and associating with Kanchipurna, a saintly devotee he had known and respected from a young age, all the while paying little attention to his wife and his family duties. Though Ramanuja beseeched Kanchipurna to be his guru, the latter humbly declined and instead deferred him to Mahapurna for further training. Thus, one year after Yamuna’s grand departure, Ramanuja was formally brought into the Vaishnava fold in a rite in which Mahapurna impressed the seal of Vishnu’s conch on his arms. For the following six months in Kanchipuram, he studied with Mahapurna the sacred Divya Prabandham, 4,000 devotional Tamil verses composed by the twelve Alvar saints. §
The Thirunarayanapuram Temple in Melkote, a sacred kshetra in Karnataka where Ramanuja resided for twelve years.§
Meanwhile, Rakshambal was understandably disturbed by her husband’s indifference to their life together since his return from Srirangam. Unwavering in her brahmin orthodoxy, she was also irreconcilably opposed to his mingling with Kanchipurna and other non-brahmins. There were several incidents in which she insulted non-brahmins, including Kanchipurna, his wife and Mahapurna. Unable to endure this, Ramanuja, still somber over his guru’s death, separated from her, sending her home to her parents. §
Resolving that he had had enough of worldly life, Ramanuja undertook the rites for entering into the holy order of sannyasins at the Varadaraja Temple in the company of Kanchipurna, with the Deity, Lord Varadaraja, as his guru. Thereafter, staying for some time as head of the monastery in Kanchi, he began giving discourses on Vedanta and Vaishnavism to the many disciples who were drawn to his presence. §
To complete his conversion to Vaishnavism, Ramanuja was encouraged by Mahapurna to seek initiation from Thirukottiyur Nambigal (a.k.a. Gostipurna) into formal recital of the sacred eight-syllable mantra, Om Namo Narayanaya. Nambigal taught Ramanuja the meaning of Charama shloka, the noblest of all passages in the Bhagavad Gita. However, he hesitated to give him mantra initiation. Ramanuja had to make eighteen trips seeking this initiation before gaining the confidence of the guru, who swore him to secrecy before imparting the mantra. “Ramanuja! Keep this mantra a secret. It is powerful. Share it only with disciples who have proven themselves worthy.” Ramanuja promised his guru that he would not share it—but it was a promise he could not keep. §
Desiring that all souls might enjoy the eternal bliss of Lord Narayana, Ramanuja immediately called all the village together, irrespective of caste and creed, to assemble in front of a temple. Standing atop the entrance gate with the gopuram towering behind him, he shouted out the mantra at the top of his voice. This blatant disobedience to his guru was an unforgivable sin, one for which he could be condemned, but Ramanuja was willing to suffer personal torment if his transgression meant that millions of people could attain salvation by hearing the sacred mantra. When Nambigal learned of this, he became angry; but when Ramanuja stood before him and clasped the guru’s feet in humility, he realized the extent of his devotee’s selfless compassion, then embraced Ramanuja and blessed him. §
At Home in Srirangam§
Ramanuja settled in Srirangam. After further training from Yamuna’s disciples, he succeeded the great Yamunacharya as administrator of Srirangam Math and Temple. He conversed with the temple Deity, Lord Sriranganathan, more than once. During one conversation the Lord granted him the title Udaiyavar, owner—possessor of mukti (salvation) and Vaikuntha (Lord Vishnu’s heavenly abode). In gracious response, Ramanuja requested the Lord to grant these blessings to all His devotees. While at Srirangam Yatiraja (as Ramanuja was known in later years) gave discourses on the hymns of the Alvar saints, preached his Vishishtadvaita philosophy and composed important philosophical works in Sanskrit. He also held debates with leading advocates of opposing schools of thought, defeating and winning them over to his way of thinking. §
Ramanuja seeks the blessings of Lord Varadaraja in Kanchi, having renounced worldly life and taken initiation to enter into the holy order of Hindu sannyasins as a lifetime celibate monk.§
As explained by Vedic Knowledge Online, “Thousands of people flocked to him every day to hear his lectures. He cleansed the temples, settled the rituals to be observed in them, and rectified many social evils which had crept into the community. He had a congregation of 700 sannyasins, 74 dignitaries who held special offices of ministry, and thousands of holy men and women who revered him as Guru. He inducted lakhs of people to the path of bhakti and a highly moral and disciplined life. He gave initiation to all people. He was now seventy years old, but was destined to live many more years, establish more maths, construct more temples and spread his teachings to many more thousands of people.”§
Ramanuja’s most significant literary work was his commentary on Badaranaya’s Vedanta Sutra, the earliest known (ca 400 bce) systematization of Vedanta. Its aphorisms are extremely terse and philosophically cryptic, without explanation. Closely referencing Bodhayana’s seminal commentary of the Sutra, Ramanuja explained and interpreted the verses according to the devotional philosophy of his tradition. §
As he commenced the work, entitled Shri Bhashya, Ramanuja told his disciples: “I can now refute the doctrines of these wrong-headed persons who think that the mere intellectual understanding of the great Vedic statements like ‘That thou art’ and ‘I am Brahman’ is enough for final beatitude of liberation. I have also to explode the views of those Jnana-karma-Samucchayavadins who admit the great efficacy of yajna, dana, tapas and karma along with the understanding of these statements. I have to establish that the purport of the Vedas and the Vedanta is the attainment of liberation through dhyana, upasana and bhakti. For all this, I shall begin writing the Shri Bhashya” (from Life of Shri Ramanuja, by Swami Ramakrishnananda, Ramakrishna Math, Chennai).§
All-India Pilgrimage§
Swami Tapasyananda provides a summary of Ramanuja’s travels following his magnum opus. “After completing the Shri Bhasya, accompanied by a large number of his disciples, Ramanuja went on an all-India pilgrimage, which was also of the nature of a digvijaya [victory tour], confronting philosophers of other schools of thought and spreading Vaishnavism among them. He first visited all the holy centers of Tamil land and of Kerala and gradually moved northward—visiting Dvaraka, Mathura, Vrindavana, Shalagrama, Saketa, Badarikasrama, Naimisa, Puskara and at last the Sharadapitha in Kashmir. The Pandits of Sharadapitha had acrimonious debates with him, but he was able to convert the ruler of Kashmir to his faith. Here Ramanuja had a vision of Hayagriva, one of the Divine Incarnations. Then he went to Kasi, where he stayed for some time and won over many learned men to his faith. Continuing south to Shripurushottama-Kshetra, now known as Puri, he founded there a monastery called Embar Math. The scholars of that place, who controlled the temple, refused to face him in debate for fear of defeat. He next went to Ahobila, situated on Garuda mountain, where he established a monastery. Next he worshiped Narasimha-Murti at Isalinga, and afterwards reached the temple of Venkatachalapati at Tirupati. There he settled, through his superhuman powers, a dispute on the question whether the image of the temple was of Siva or Vishnu, in favor of Vaishnavas. He then returned to Srirangam via his old residence of Kanchipuram where he did obeisance to Varadaraja.”§
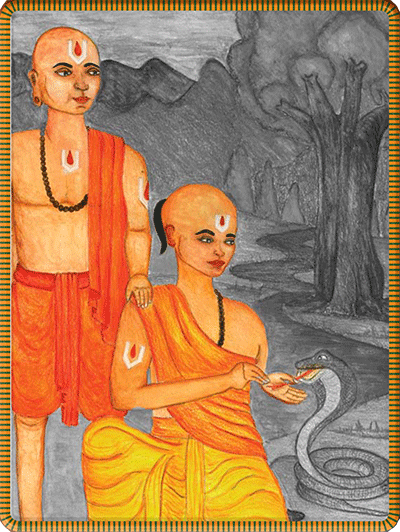
To Ramanuja’s amazement, Govinda, fearless and full of compassion, removes a thorn that has pierced the tongue of a deadly cobra.§
Twelve Years in Melkote, Karnataka§
Ramanuja’s influence grew in the years to follow, and he gained a huge number of followers. Yadava and other advaitins, including the Chola king Kulothunga I (who considered him a threat to Saivism) continued to plot against him. The king intended to force this leader of Vashnavism to sign a declaration endorsing Lord Siva as the supreme God. When the king summoned Ramanuja to his court, Ramanuja’s shishyas convinced him to flee to safety. He escaped to Melkote, in Karnataka, where he is credited with rebuilding and renovating the Thirunarayanapuram Temple. There he gained the favor of the Jain king Bitrideva of the Hoysala dynasty by curing his daughter of an illness. Later, in a visionary dream, Lord Narayanan told him He was buried in the ground under a nearby anthill. Bitrideva helped Ramunuja recover the statue of the Lord, which had earlier been thrown out of the temple by Muslim invaders. Ramanuja reinstalled the sacred murti in the sanctum, where it remains to this day. §
Ramanuja still needed an utsava murti, a Deity image made specifically to be paraded through the streets during festivals. This was needed in order to celebrate festivals properly. Once again the Lord appeared in his dreams, this time telling him the temple’s original utsava murti of Cheluvanarayana was currently in the possession of a sultan in Delhi. Ramanuja, now 80 years old, made the tiring journey to Delhi and asked the king to return the murti. The king asked him to identify it, but it could not be found. §
Ramanuja called out, “Adiyen Vareer Enthan Selva Pillai” (“Please come out, my darling child). Miraculously, the three-foot-tall Cheluvanarayana statue came running from the chamber of the princess and sat on Ramanuja’s lap. Ramanuja brought Him back to Thirunarayanapuram—followed by the Muslim princess, who could not bear to be separated from her beloved Lord. She remained in Melkote serving Narayana to the end of her life. To this day she is honored at the temple there as Bibi Nachiyar.§
Ramanuja scribes his commentary on the Brahma Sutras, formulating a Vishishtadvaita interpretation of this terse summation of Vedanta written by Badarayana around 400 bce.§
Ramanuja remained in Thirunarayanapuram for twelve years. As the administrator of temple activities, he devoted himself to community development and introduced several new festivals, including the Diamond Crown Festival. He involved the people of Melkote in all temple activities, daily pujas, rituals and annual festivals, embracing people of every caste and economic status in the service of Thirunarayana. He called the tribal people thirukulathatar, “family members of Goddess Lakshmi.” He was loved and respected by one and all. §
When the cruel king Kulothunga I finally passed away, Ramanuja desired to return to his beloved Srirangam. But the people of Melkote begged him to stay in Thirunarayanapuram. In response, Ramanuja created a bronze image of himself which was formally installed in a shrine in the temple. He also brought 52 Bhattars (priests) from Srirangam to perform the daily worship. To this day the priests carry out all temple activities according to the traditions set forth by him. There he is equally revered with the Deity Thirunarayana, and his birthday is grandly celebrated each year. Shri Vaishnavas seek blessings from the bronze Ramanuja murti before worshiping at the Deity sanctums.§
Nine Literary Works
 amanuja wrote to fulfill the wishes of Yamunacharya and to fulfill the vision of Ubhaya Vedanta. His nine books are considered to be nine precious gems (navaratna) in the world of Vaishnavite Hindu philosophy. 1) Vedanta Sangraha, an exposition of Vedanta; 2) Shri Bhashya, a commentary on the Brahma Sutras; 3) Vedanta Sara (Essence of Vedanta), an appendix to Shri Bhashya; 4) Vedanta Dipa (Light of Vedanta), another appendix and commentary to Shri Bhashya; 5) Gadhya Thrayam (or Vaikunta Gatyam), a description of Vaikuntha (the abode of Vishnu); 6) Shri Ranga Gadhyam, a prayer surrendering to the feet of Sriranganatha; 7) Saranagati Gadhyam, an imaginary dialogue between Ramanuja, Lakshmi and Narayana; 8) Nithya Grantham, daily activities to be performed by Vaishnavas; and 9) Gita Bhashya, a commentary on the Bhagavad Gita. §
amanuja wrote to fulfill the wishes of Yamunacharya and to fulfill the vision of Ubhaya Vedanta. His nine books are considered to be nine precious gems (navaratna) in the world of Vaishnavite Hindu philosophy. 1) Vedanta Sangraha, an exposition of Vedanta; 2) Shri Bhashya, a commentary on the Brahma Sutras; 3) Vedanta Sara (Essence of Vedanta), an appendix to Shri Bhashya; 4) Vedanta Dipa (Light of Vedanta), another appendix and commentary to Shri Bhashya; 5) Gadhya Thrayam (or Vaikunta Gatyam), a description of Vaikuntha (the abode of Vishnu); 6) Shri Ranga Gadhyam, a prayer surrendering to the feet of Sriranganatha; 7) Saranagati Gadhyam, an imaginary dialogue between Ramanuja, Lakshmi and Narayana; 8) Nithya Grantham, daily activities to be performed by Vaishnavas; and 9) Gita Bhashya, a commentary on the Bhagavad Gita. §
All nine works were written in Sanskrit. Though Ramanuja spoke and discoursed in the Tamil language, he does not seem to have written anything in his native tongue.§
His Final Message§
Returning to Srirangam, the aged acharya continued to serve Lord Sriranganathan and all His devotees. As a polemicist and philosopher, he devoted the remainder of his life to proving the Vedantic legitimacy of the popular conception of a personal Deity with an approachable identity. §
At the ripe age of 120, Ramanuja prayed to Sriranganathan for moksha, liberation. His parting words to his devoted disciples were: §
“Worship holy men exactly as you would do in the case of your spiritual preceptor. Have sincere faith in the teachings of the great Acharyas of yore. Never be slaves to your senses. Be not satisfied with the acquisition of worldly knowledge. Go on reading repeatedly the books dealing with the greatness of God and the wonders of His creation. If perchance you are favored with scintillating wisdom by the guru’s grace, then the attraction of the senses will cease for you. Learn to treat all your feelings with indifference. Enjoy the utterance of the names and glories of God’s devotees with as much relish as the utterance of God’s names and glories. Bear in mind that he who renders service to God’s devotees attains God speedily. Therefore, unless you dedicate yourself to the service of God and His devotees, you will not be saved, however wise you may be. Do not consider the life of a Vaishnava as a means for acquiring any selfish advantage. You must endeavor to realize the ideal.§
This granite murti of Sri Ramanuja is enshrined in the Cheluvanarayan Vishnu Temple at Melkote.§
“Devote a portion of the day, at least one hour, to the contemplation of the greatness of your spiritual preceptor and some time every day to the reading of the sacred writings of the alvars or the acharyas. Always seek the company of those that pursue the path of self-surrender to God and avoid the company of those that say, ‘There are other paths leading to salvation.’ Do not associate with people who are always in quest of filthy lucre and sense enjoyment, but mingle with the devotees of God to the extent possible. Whoever looks upon the sacred images of God as mere stones, his own spiritual teacher as an ordinary human being, eminent devotees as high or low according to the caste of their birth, the holy water that has touched the feet of God and has as a consequence acquired the power to purify and purge one of all sins as ordinary water, the sacred mantras as a collection of sounds, and the Supreme Lord of all the worlds as one not higher than the Devas—let him be considered an unworthy person fit only for purgatory” (from Sri Ramanuja, Swami Tapasyananda).§
Near the same temple, Ramanuja discovered and unearthed the parade murti of Lord Cheluvanarayana which was thrown out of the temple centuries before by Muslim mauraders.§
Influence Today
 wami Tapasyananda provides this summary: “It is important to point out that Ramanuja’s devotional philosophy had in a way a much wider field of operation than South India or Tamil Nadu. Many sects of North Indian Vaishnavism also had their origin in his teaching. Ramananda (1300-1411), the fountainhead of monotheism and Rama cults of North India, was a follower of Ramanuja’s sect and was initiated into Vishishtadvaita. He went early on pilgrimage to the North and stayed there for several years. On his return, the caste-conscious Vaishnavas of the South could not entertain him in their community. He was a spiritual liberalist who did not recognize caste as a factor in spiritual competence. Therefore he settled in Benares, and was practically the guru, the spiritual stimulator, of the twelve great leaders of the Vaishnava cult of the North. They belonged to all castes and included a cobbler and a Muslim. The most illustrious of them was Kabir, who worked for the unification of Vaishnavaism and Islamic monotheism. Another disciple, Ravidas, a cobbler by birth, initiated the celebrated Mira Bai into the meaning of bhakti. Sena, a barber by caste, converted the Raja of Bandogarh into Vaishnavism. Dana was a Jat, and Pipa a Rajput prince. In later days, great leaders of monotheistic devotion, like Tulsidas and Dadu, got their inspiration from Ramanuja’s teachings.”§
wami Tapasyananda provides this summary: “It is important to point out that Ramanuja’s devotional philosophy had in a way a much wider field of operation than South India or Tamil Nadu. Many sects of North Indian Vaishnavism also had their origin in his teaching. Ramananda (1300-1411), the fountainhead of monotheism and Rama cults of North India, was a follower of Ramanuja’s sect and was initiated into Vishishtadvaita. He went early on pilgrimage to the North and stayed there for several years. On his return, the caste-conscious Vaishnavas of the South could not entertain him in their community. He was a spiritual liberalist who did not recognize caste as a factor in spiritual competence. Therefore he settled in Benares, and was practically the guru, the spiritual stimulator, of the twelve great leaders of the Vaishnava cult of the North. They belonged to all castes and included a cobbler and a Muslim. The most illustrious of them was Kabir, who worked for the unification of Vaishnavaism and Islamic monotheism. Another disciple, Ravidas, a cobbler by birth, initiated the celebrated Mira Bai into the meaning of bhakti. Sena, a barber by caste, converted the Raja of Bandogarh into Vaishnavism. Dana was a Jat, and Pipa a Rajput prince. In later days, great leaders of monotheistic devotion, like Tulsidas and Dadu, got their inspiration from Ramanuja’s teachings.”§
From Ramanuja.org, we read, “Ramanuja’s supreme effort resulted in a systematic presentation of Vishishtadvaita. His genius also led to the development of a complete system which synthesizes the concept of God with the philosophy of the impersonal Absolute. The followers of Ramanuja are called Shri Vaishnavas. This term is not exclusive to Iyengars (a major sect among Brahmins of South India). Also among South Indians are a set of followers called Shattada Shri-Vaishnavas of non-Brahmin origins. Followers of Ramanuja (or at least those who include him in the lineage of their earlier acharyas) can be seen far and wide in different parts of India including Gaudiya Vaishnavas of Bengal and the Swaminarayans of Gujarat.”§
Vaishnava pathashalas and colleges all over India, as well as elsewhere, include Ramanuja’s philosophy in their curricula. Several Vaishnava organizations are propagating Shri Vaishnavism in Europe, Russsia and North and South America. The tradition begun by Ramanuja of reciting Divya Prabandham continues in Sriranganadhar’s temple and other Vishnu temples to this day. Sriperumbudur’s Adhikesava Perumal temple at Ramanuja’s birthplace is one of the holiest places of worship for Shri Vaishnavites. Ramanuja is equally revered with the Perumal Deity there, and a bronze statue of Ramanuja is under the same roof as Adhikesava, Shridevi and Bhudevi. There is a small shrine to Ramanuja next to the temple. In virtually all Vaishanava temples there is statue of Ramanujacharya, including Mukthinath, Nepal, where Ramanujacharya himself installed the main Deity icon, which is made of saligram. §
Swami Vivekananda, who introduced Hindu thought to the Western world at the turn of the twentieth century, commented, “Ramanuja, with a most practical philosophy, great appeal to the emotions, an entire denial of birthrights before spiritual attainments and appeals through the popular tongue, completely succeeded in bringing the masses back to the Vedic religion.” (The Historical Evolution of India). §
This speaks volumes about Ramanuja as a great visionary, a humanitarian, a philosopher and a guru. §
Resources§
Sri Ramanuja, His Life, Religion & Philosophy, by Swami Tapasyananda, Sri Ramakrishna Math, Mylapore, Madras§
Life of Sri Ramanuja, by Swami Ramakrishnananda, Sri Ramakrishna at, Mylapore, Madras, 1959 (translated from Bengali by Swami Budhananda)§
The Life of Ramanujacharya, the Exponent of the Vishishtadvaita Philosophy, by Akondaville Govindacharya, Kapalee Press, Madras, 1906§
ABOUT THE AUTHORS§
Lakshmi and Tim Sridharan were brought up with great emphasis on Hindu traditions, culture and values by devout Tamil Brahmin parents in Madras, Tamil Nadu, and now live in San Jose, California. In preparation for this article, they traced the life path of Ramanuja through Tamil Nadu and Karnataka during a visit to India in December of 2013. While this is their first joint venture in writing, Lakshmi has published many articles on a variety of subjects, including Indian tradition and culture.§